The government has announced that National Insurance is being raised by 1.25% for employers and employees, the levy will also apply to individuals above State Pension age with employment income or profits from self-employment above £9,568. The rate of income tax which is paid by people who receive dividend income from share will also increase by 1.25% from April 2022.
What Is National Insurance?
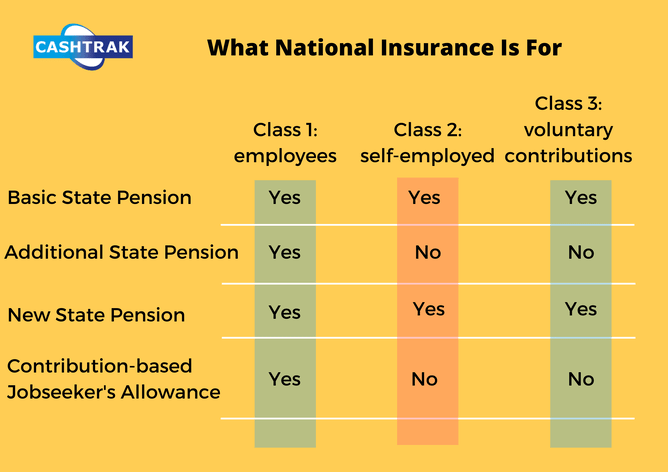
These contributions are paid to qualify you for certain benefits and the State Pension (see the table below.) Contributions are compulsory if you’re 16 or over and are either:
- an employee earning above £184 a week
- self-employed and making a profit of £6,515 per year
You need a National Insurance number before you can start paying National Insurance contributions.
Class 4 contributions paid by self-employed people with a profit of £9,569 or more do not usually count towards state benefits.
Employers Payments
Employers pay contributions on their employees earnings and benefits and are responsible for collecting employees Class 1 contributions through the PAYE scheme.
The amount paid by the employer depends on the employee’s earnings and their National Insurance category letter.
Some businesses can take advantage of the Employment Allowance scheme which allows eligible employers to reduce their annual National Insurance liability by up to £4,000.
Employers pay 13.8% for most employees above the Secondary Threshold for 2021/22, the threshold at which employers start paying National Insurance, this is currently £737, this will also increase by 1.25% for the Health and Social Care Levy.
National Insurance Classes
There are different types of National Insurance known as classes, the type you pay depends on your employment status and how much you earn.
Who Uses Your National Insurance Number?
These organisations need to know what your number is:
- HMRC
- Your employer
- If you claim state benefits:
- The Department for Work and Pensions (which includes Jobcentre Plus and the Pension, Disability and Carers Service)
- If you claim Housing Benefit:
- Your local council
- Electoral Registration Officers
- If you apply for a Student Loan:
- The Student Loan Company
- If you have a personal or stakeholder pension:
- Your pension provider
- If you have an Individual Savings Account (ISA):
- The ISA provider
- Authorised financial service providers who help you buy and sell investments like shares, bonds and derivatives
How Much You Will Pay
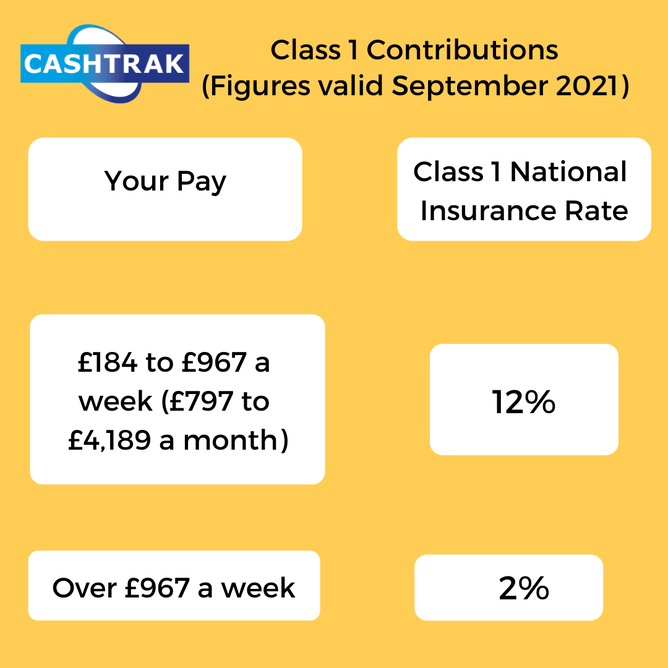
If you're employed, the rate for most people 2021/22 is:
You’ll pay less if:
you’re a married woman or widow with a valid ‘certificate of election’ or you’re deferring National Insurance because you’ve got more than one job. Employers pay a different rate of National Insurance depending on their employees’ category letters..
If you're self-employed, you pay Class 2 and Class 4 National Insurance, depending on your profits and most people pay through Self-Assessment. You may be able to pay voluntary contributions to avoid gaps in your National Insurance.
If you're employed AND self-employed, your employer will deduct your Class 1 National Insurance through your wages but you may have to pay Class 2 and 4 for your self-employed work.
Different Rules
There are different rules for:
- Company directors
- Landlords running a property business
- Share fisherman
National Insurance can get complicated! Need help, contact us 01865 522785 or info@cashtrak.co.uk.